
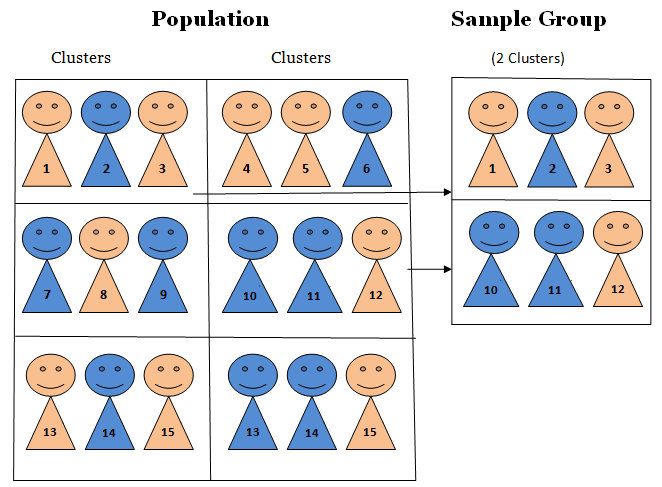
We need to select a proportional number from each group. Since these groups are not the same size, we would not just sample 200/5 = 40 from each group.

The Right-to-Know page on the ECC website has the following counts by age (as of ): We would want to get a representative sample from each age group. Suppose we want to sample 200 ECC students on a particular issue, where the responses might vary by age. Sample of 4 should have 1 blue, 1 green, and 2 reds.įor another take, watch this YouTube video: Working things out, we can see that a stratified (by color) random Individuals in the population are blue, so 1/4 of the sample should be blueĪs well. The number selected should be proportional.

(Man, that's a weird word!) The key here is that Once we have the strata determined, we need to decide how many individuals We can easily separate the individuals by color. Visually, it might look something like the image below. Within each group should be similar in some way. Obtaining a proportional simple random sample from each group. The population into non-overlapping groups called strata and then Using some characteristic, and then take a proportional random sample fromĪ stratified sample is obtained by separating With this technique, we separate the population Most of the researches are done in different stages with each stage applying a different random sampling technique.Do you remember how simple random sampling works? Visually, it's just numberingĮach individual and randomly selecting a certain number of them. In most of the complex researches done in the field or in the lab, it is not suited to use just a single type of probability sampling. This probability sampling technique involves a combination of two or more sampling techniques enumerated above. The researcher can either include all the individuals within the selected areas or he can randomly select subjects from the identified areas.It is important that all areas (countries) within the population be given equal chances of being selected. The researcher randomly selects a number of identified areas.
In cluster sampling, the research first identifies boundaries, in case of our example it can be countries within Asia.Just imagine doing a simple random sampling when the population in question is the entire population of Asia. Cluster Random SamplingĬluster random sampling is done when simple random sampling is almost impossible because of the size of the population. There is no clear advantage when using this technique. You subjects will be patients 3, 8, 13, 18, 23, and so on.Select another integer which will be the number of individuals between subjects e.g.The first thing you do is pick an integer that is less than the total number of the population this will be your first subject e.g.Say for example you are in a clinic and you have 100 patients. Systematic random sampling can be likened to an arithmetic progression wherein the difference between any two consecutive numbers is the same. It is also preferred over the simple random sampling because it warrants more precise statistical outcomes. Researchers usually use stratified random sampling if they want to study a particular subgroup within the population. It is important to note that all the strata must have no overlaps. Then, the researcher randomly selects the final list of subjects from the different strata. This is a probability sampling technique wherein the subjects are initially grouped into different classifications such as age, socioeconomic status or gender. Stratified random sampling is also known as proportional random sampling.
#Random sampling techniques software#
It can be as mechanical as picking strips of paper with names written on it from a hat while the researcher is blindfolded or it can be as easy as using a computer software to do the random selection for you. All the researcher needs to do is assure that all the members of the population are included in the list and then randomly select the desired number of subjects. Simple random sampling is the easiest form of probability sampling. Types of Probability Sampling Simple Random Sampling


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
